zcurve is used to fit z-curve models. The function
takes input of z-statistics or two-sided p-values and returns object of
class "zcurve" that can be further interrogated by summary and plot
function. It default to EM model, but different version of z-curves can
be specified using the method and control arguments. See
'Examples' and 'Details' for more information.
zcurve(
z,
z.lb,
z.ub,
p,
p.lb,
p.ub,
data,
method = "EM",
bootstrap = 1000,
parallel = FALSE,
control = NULL
)Arguments
- z
a vector of z-scores.
- z.lb
a vector with start of censoring intervals of censored z-scores.
- z.ub
a vector with end of censoring intervals of censored z-scores.
- p
a vector of two-sided p-values, internally transformed to z-scores.
- p.lb
a vector with start of censoring intervals of censored two-sided p-values.
- p.ub
a vector with end of censoring intervals of censored two-sided p-values.
- data
an object created with
zcurve_data()function.- method
the method to be used for fitting. Possible options are Expectation Maximization
"EM"and density"density", defaults to"EM".- bootstrap
the number of bootstraps for estimating CI. To skip bootstrap specify
FALSE.- parallel
whether the bootstrap should be performed in parallel. Defaults to
FALSE. The implementation is not completely stable and might cause a connection error.- control
additional options for the fitting algorithm more details in control EM or control density.
Value
The fitted z-curve object
Details
The function returns the EM method by default and changing
method = "density" gives the KD2 version of z-curve as outlined in
Bartoš and Schimmack (2022)
. For the original z-curve
(Brunner and Schimmack 2020)
, referred to as KD1, specify
'control = "density", control = list(model = "KD1")'. Specifying
the lower and upper bounds of z-scores or p-values will fit the censored
version of z-curve described in (Schimmack and Bartoš 2023)
.
References
Bartoš F, Schimmack U (2022).
“Z-curve 2.0: Estimating replication rates and discovery rates.”
Meta-Psychology, 6.
doi:10.15626/MP.2021.2720
.
Brunner J, Schimmack U (2020).
“Estimating population mean power under conditions of heterogeneity and selection for significance.”
Meta-Psychology, 4.
doi:10.15626/MP.2018.874
.
Schimmack U, Bartoš F (2023).
“Estimating the false discovery risk of (randomized) clinical trials in medical journals based on published p-values.”
PLoS ONE, 18(8), e0290084.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0290084
.
See also
Examples
# load data from OSC 2015 reproducibility project
OSC.z
#> [1] 2.409175 3.245251 2.164192 3.191229 2.702059 3.137051 8.402858
#> [8] 3.718460 4.293275 3.512496 1.973777 7.066053 4.383039 3.536266
#> [15] 3.392537 2.194877 3.059374 4.637228 3.982280 2.169338 1.946709
#> [22] 2.268213 4.180570 3.459550 3.731395 1.836848 3.100000 10.000000
#> [29] 2.967738 2.183487 2.408916 2.365618 2.257129 1.968592 3.909901
#> [36] 2.273435 10.000000 2.307984 2.290368 2.967738 2.014091 10.000000
#> [43] 10.000000 3.290527 2.432379 2.014091 2.575829 10.000000 2.307984
#> [50] 2.967738 2.967738 1.792831 3.290527 1.959964 2.297408 2.053749
#> [57] 10.000000 2.542699 2.403655 10.000000 3.410733 2.975294 3.849639
#> [64] 10.000000 2.273435 2.106589 3.694892 2.195944 2.307984 4.178900
#> [71] 1.951480 2.967738 2.226212 2.290368 2.967738 2.780638 2.612054
#> [78] 10.000000 2.652070 10.000000 2.725494 2.652070 3.042724 2.652070
#> [85] 2.970656 2.257129 2.386708 3.403461 2.120072 2.688852
# fit an EM z-curve (with disabled bootstrap due to examples times limits)
m.EM <- zcurve(OSC.z, method = "EM", bootstrap = FALSE)
#> Warning: The z-curve method is meant for large samples of test statistics. It might produce undercoverage and biased estimates of EDR in small sample sizes.
# a version with 1000 boostraped samples would looked like:
m.EM <- zcurve(OSC.z, method = "EM", bootstrap = 1000)
#> Warning: The z-curve method is meant for large samples of test statistics. It might produce undercoverage and biased estimates of EDR in small sample sizes.
# or KD2 z-curve (use larger bootstrap for real inference)
m.D <- zcurve(OSC.z, method = "density", bootstrap = FALSE)
#> Warning: The z-curve method is meant for large samples of test statistics. It might produce undercoverage and biased estimates of EDR in small sample sizes.
# inspect the results
summary(m.EM)
#> Call:
#> zcurve(z = OSC.z, method = "EM", bootstrap = 1000)
#>
#> model: EM via EM
#>
#> Estimate l.CI u.CI
#> ERR 0.618 0.454 0.750
#> EDR 0.384 0.077 0.703
#>
#> Model converged in 24 + 163 iterations
#> Fitted using 73 z-values. 90 supplied, 85 significant (ODR = 0.94, 95% CI [0.87, 0.98]).
#> Q = -60.61, 95% CI[-71.14, -46.69]
summary(m.D)
#> Call:
#> zcurve(z = OSC.z, method = "density", bootstrap = FALSE)
#>
#> model: KD2 via density
#>
#> Estimate
#> ERR 0.613
#> EDR 0.506
#>
#> Model converged in 46 iterations
#> Fitted using 73 z-values. 90 supplied, 85 significant (ODR = 0.94, 95% CI [0.87, 0.98]).
#> RMSE = 0.11
# see '?summary.zcurve' for more output options
# plot the results
plot(m.EM)
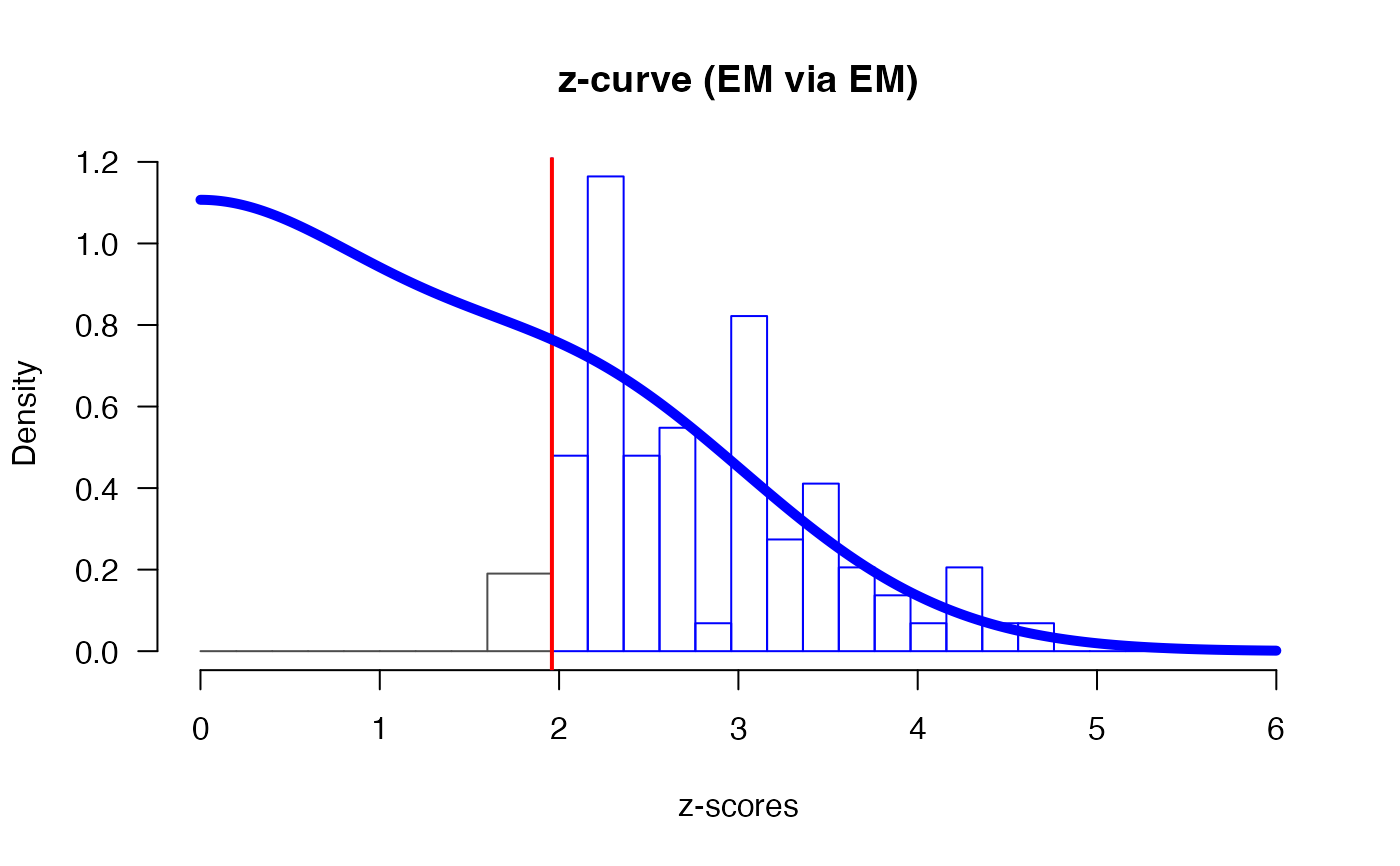 plot(m.D)
plot(m.D)
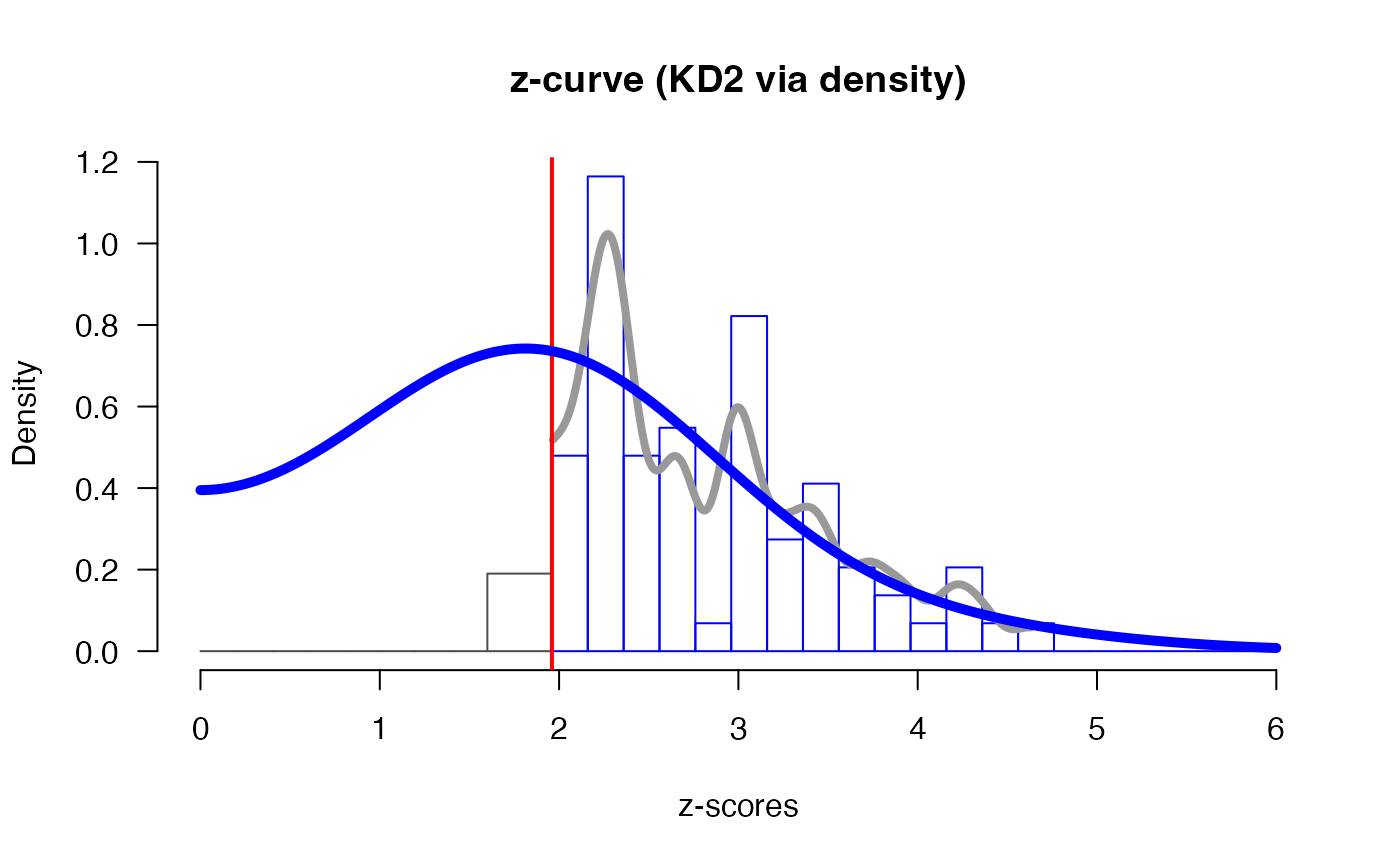 # see '?plot.zcurve' for more plotting options
# to specify more options, set the control arguments
# ei. increase the maximum number of iterations and change alpha level
ctr1 <- list(
"max_iter" = 9999,
"alpha" = .10
)
if (FALSE) m1.EM <- zcurve(OSC.z, method = "EM", bootstrap = FALSE, control = ctr1) # \dontrun{}
# see '?control_EM' and '?control_density' for more information about different
# z-curves specifications
# see '?plot.zcurve' for more plotting options
# to specify more options, set the control arguments
# ei. increase the maximum number of iterations and change alpha level
ctr1 <- list(
"max_iter" = 9999,
"alpha" = .10
)
if (FALSE) m1.EM <- zcurve(OSC.z, method = "EM", bootstrap = FALSE, control = ctr1) # \dontrun{}
# see '?control_EM' and '?control_density' for more information about different
# z-curves specifications